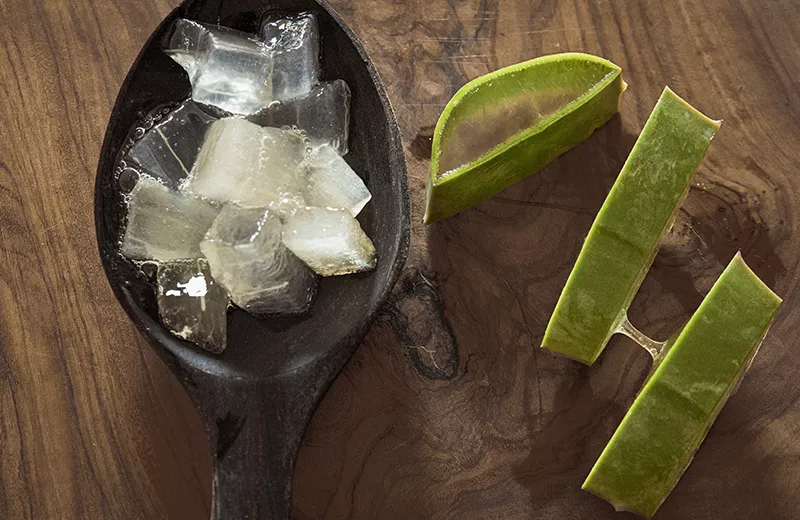
Aloe Vera Skin
The outer part or skin of the Aloe Vera leaf consists of 15-20 cells, also known as the plant’s protective layer. This outer layer synthesizes proteins and carbohydrates and protects the inner gel from bacteria, parasites, and environmental elements such as wind, rain, and sun. The skin is not typically used because it contains certain compounds that can harm humans when ingested.
Aloe Vera Skin Toxicity
The skin of the Aloe Vera plant contains a compound called aloin, or barbaloin, a yellowish-brown substance found in the outer leaf of the plant. Aloin is known to have laxative properties and was once used in over-the-counter (OTC) laxative products. However, the FDA banned its use in OTC laxatives in 2002 due to concerns about safety and a lack of definitive information about its potential risks. Aloin can cause cramping, diarrhea, and other digestive issues if consumed in large quantities.
Is it Safe to Use Aloe Vera Skin?
While the skin of the Aloe Vera plant can be harmful if ingested, it is generally considered safe for topical use. The skin can be used for minor burns, sunburns, and psoriasis. However, it’s important to note that some people’s skin can cause allergic reactions. Therefore, doing a patch test before using it on the skin is recommended.
Aloe Vera Gel vs. Aloe Vera Skin
Most of the beneficial properties of Aloe Vera come from the gel, not the skin. The gel contains most of the bioactive compounds in the plant, including vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and antioxidants. Therefore, when using Aloe Vera for its health benefits, it’s typically the gel, not the skin.
While Aloe Vera skin may not have the same beneficial nutrients as the inner gel, it can still offer some therapeutic benefits for topical use. However, it’s essential to be aware of the possible side effects and risks, especially for those with allergies or sensitivities.